What is Diagnostic Trouble Codes (OBD-II) for your Cars?

The first generation of OBD systems, though, had limited diagnostic capabilities. However, the second generation, used in today automobiles since the mid 1990s, has the ability not only to monitor many more systems, but can tell when a particular electrical connection in a circuit is not functioning properly and point you in that direction. That is, if you know how to access this trouble code. Automotive technicians have been doing it for years. Home mechanics have been doing it for years. And you can too.
How can You Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (OBD-II)?
Retrieving the code is not difficult. In fact, you can do it at home too using the correct procedure
An easier option is to buy a code reader or scan tool and plug it into the data link connector to access these codes. You can use this tool to gain access to codes on second generation OBD systems. There are many sophisticated scan tools on the market, but even a simple code reader or scan tool will help you retrieve many diagnostic trouble codes for cars.
How do You Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes?
The computer compares these electrical signals from electrical connectors, sensors, and other components to its data bank in memory. If one of the received signals doesn’t match the value in memory, it assigns it a predetermined trouble code and alerts you by turning on the Engine Check light or Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) on your dashboard.
This trouble code is composed of a letter and four numbers. It may look something like this: P0136. The letter at the beginning of the code points to the overall function of the system involved in the problem. In this case, the powertrain. The next digit could be a number 0–assigned to a standard type of code–or a number 1, which is an especific car manufacturer code.
The next number tells you the function of the component that registered the problem. In our example, it is telling you the component involved measures the fuel and air content going into the engine. Finally, the next 2 digits point you to the component or circuit in question and the type of problem it detected. In this case, it is telling you the downstream heated oxygen sensor in the Bank 1 section has either detected a problem with the air/fuel mixture or the component itself has stopped working properly.
Armed with this information, an automotive technician or home mechanic can proceed to troubleshoot the component itself, its circuit, or the reason for the imbalance in the air/fuel mixture.
OBD-ii Data Link Connector
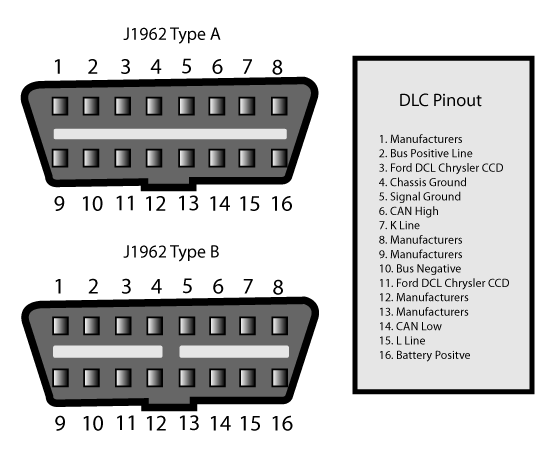
Where to Find the Exact Meaning of the Codes?
Also, many vehicle service manuals now come with a list of OBD-ii system codes. You can buy this manual at your local auto parts store or consult one by visiting the reference section of your local public library. In addition, several online sites provide a list of diagnostic trouble codes for your cars and their meaning for free–see the Reference section below.
Once you know what the trouble code means, you have several options. If you like to do your own car repairs, you can troubleshooting and try to fix the problem yourself with the help of your vehicle service manual. Car manuals not only tell you how the different systems and components in your vehicle operate, but give you information about locating and troubleshooting many of these components in a step by step procedure. Still, you may decide to take your vehicle to a car shop and use this information to request repair estimates to different auto repair shops to make an informed decision.

